Several more standards are ready and in development for seamlessly using federated computational resources
and shared data. These standards will enable clinicians and researchers to leverage
the world's genomic data in a much more automatic and advanced manner than we
can imagine today. Future genomics is greatly about successfully
enabling data sharing and the use of advanced pattern matching to its broadest
potential. Henceforth it is also vital to ensure that the legal frameworks are flexible
enough to mirror patients' interest, those whose only hope often relies on an effective
cooperation between labs around the world.
Asynchronous Matchmaker exchange - a digital solution for sharing experiences on rare genomic variants

The Matchmaker Exchange (MME) can be seen as a part of the first steps towards the GA4GH vision of an "Internet of genomics" and has recently been implemented at Oslo University Hospital.
an "Internet of genomics"
MME has recently been implemented at Oslo University Hospital to enable matchmaking of genotypic and phenotypic information for consented rare diseases cases, in the first instance with SciLifeLab at Karolinska University Hospital. A condition of this service going live is approval by the hospital’s Information Security Officer, using a risk assessment approach. Consequently, and as a part of Norway’s BigMed precision medicine project, a risk assessment was performed on this MME implementation, applying the principles of ISO 31000 and 27005 for risk identification, analysis and evaluation. Risks identified were also assessed using the local health institution’s 1) risk rating scale for information security and 2) safety principles and requirements for IT infrastructure and applications.
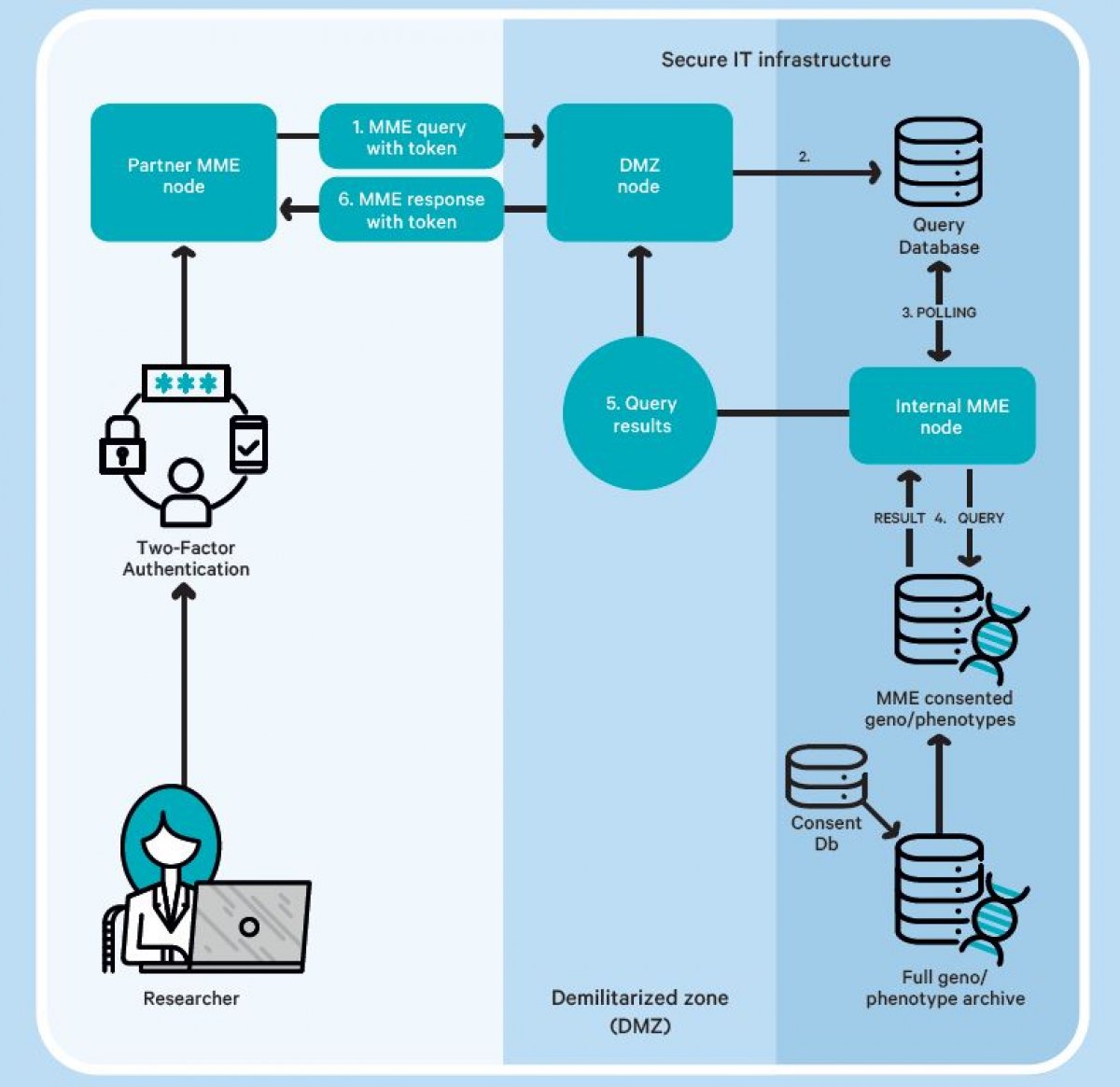
The findings of the risk assessment were presented as a poster (available HERE) at the 8th Plenary meeting of the GA4GH on the 29th of November. These were generalized to capture broader implications for other institutions looking to assure local implementations of MME, and to draw conclusions on the applicability of risk assessments for implementation of services based on federated systems for data access. Please, contact Sharmini Alagaratnam in case of any questions or further discussion about the risk assessment.
This article is relevant for clinical work within Rare diseases and that of data sharing @BigMed.
Status:
Finished
Partners:
Oslo University Hospital - Intervention center, DNV
Topics


Relevant Projects

Classified Variants are Anonymous


