Differences in variant frequencies between populations further underline the importance of large and ethnically diverse data sets. BigMed will make clinical genomics data more available and actionable through the construction of genomic databases and decision support tools.
Sharing of genomic data

Optimal implementation of precision medicine is reliant on sharing data on genes, variants and phenotypes. Access to large data sets of comparable genome information is fundamental to the ability to analyze each patient’s genetic fingerprint, and to understand the implications of individual variants.
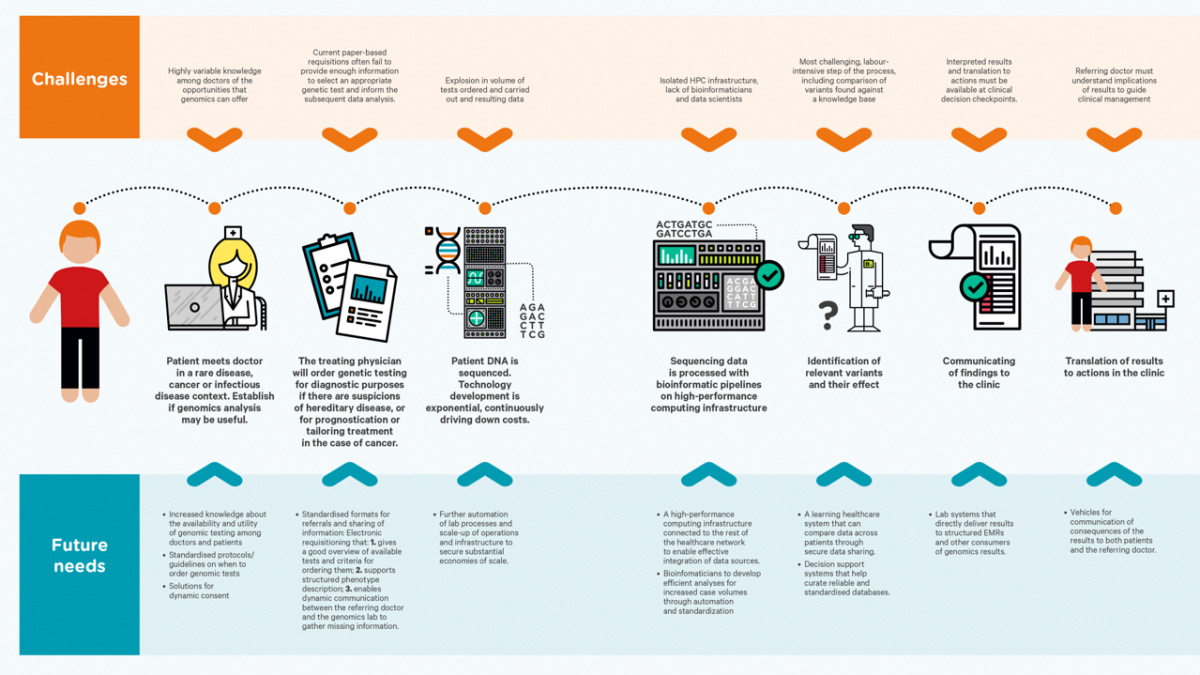
Activities and deliverables are described below.
What can be shared as anonymous data?
- Trusted Variant eXchange (TVX): Solution for sharing of classified variants with trusted partners, including conflict detection for quality assurance and shared learning between laboratories.
- Implement online sharing of single variants (GA4GH Beacon service)
Sharing of sensitive information
- Implement point of contact for queries of similar cases (secure sharing/querying of variants in context and with phenotype based on Human Phenotype Ontology via GA4GH Matchmaker exchange)
- Decision support tool for copy number variant interpretation
- Establish genome reference database (pseudonymized genome database)
- Report: Needs and requirements mapping for reference database with genome and phenotype both for clinical and research purposes.
Other
- Structured phenotyping: Mapping of relevant phenotype ontologies related to high speed pipeline.
- Report on verification and validation approaches for variant interpretation decision support software
Consent
- Consent management for genomics: Mapping of needs and requirements for “the perfect consent solution”, stakeholder mapping involving clinical needs, patient needs, regulatory requirements etc.
- Digital dynamic consent solution developed
Partners: OUS dept for medical genomics, OUS dept of tumor biology, DNV GL, OUS legal section, UiO legal faculty, UiO USIT

Relevant Projects

Digital Dynamic Consent

Variant eXchange - sharing of genomic variants classification between trusted partners

Benchmarking as a tool for quality in genetic testing
Ensuring accuracy in genomic medicineModern medical tests based on DNA and RNA sequencing are composed of a pipeline of numerous hardware systems, complex proprietary and open-source software, custom-built scripts, and manual,

Big data management for the precise treatment of three patient groups

Classified Variants are Anonymous

Clinical reporting of genomics – best practices
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is transitioning from the research environment to clinical diagnostics in a process which has proven difficult, and exome and whole genome sequencing are at the early stages of implementation in Nordic

Consent Management for Genomics
With the increased utilization of genomic sequencing in the clinical context in Norway, practical and ethical issues in the development of the content and process of informed consent (IC) are emerging. Challenges exist in bridging the

New functionality in Ella – Phenotypes and structural variants
ELLA is a software tool for clinical interpretation of genetic variants that is developed and in use at the Department of Medical Genetics at Oslo University Hospital. In BigMed, two deliveries are planned that involve expansion of the

Regulation of CDS Software
The amount of health data used in patients’ diagnosis or treatment is growing beyond a manageable level for individual clinicians. Clinical decision support (CDS) software can help to access and analyse these data and thereby assist


