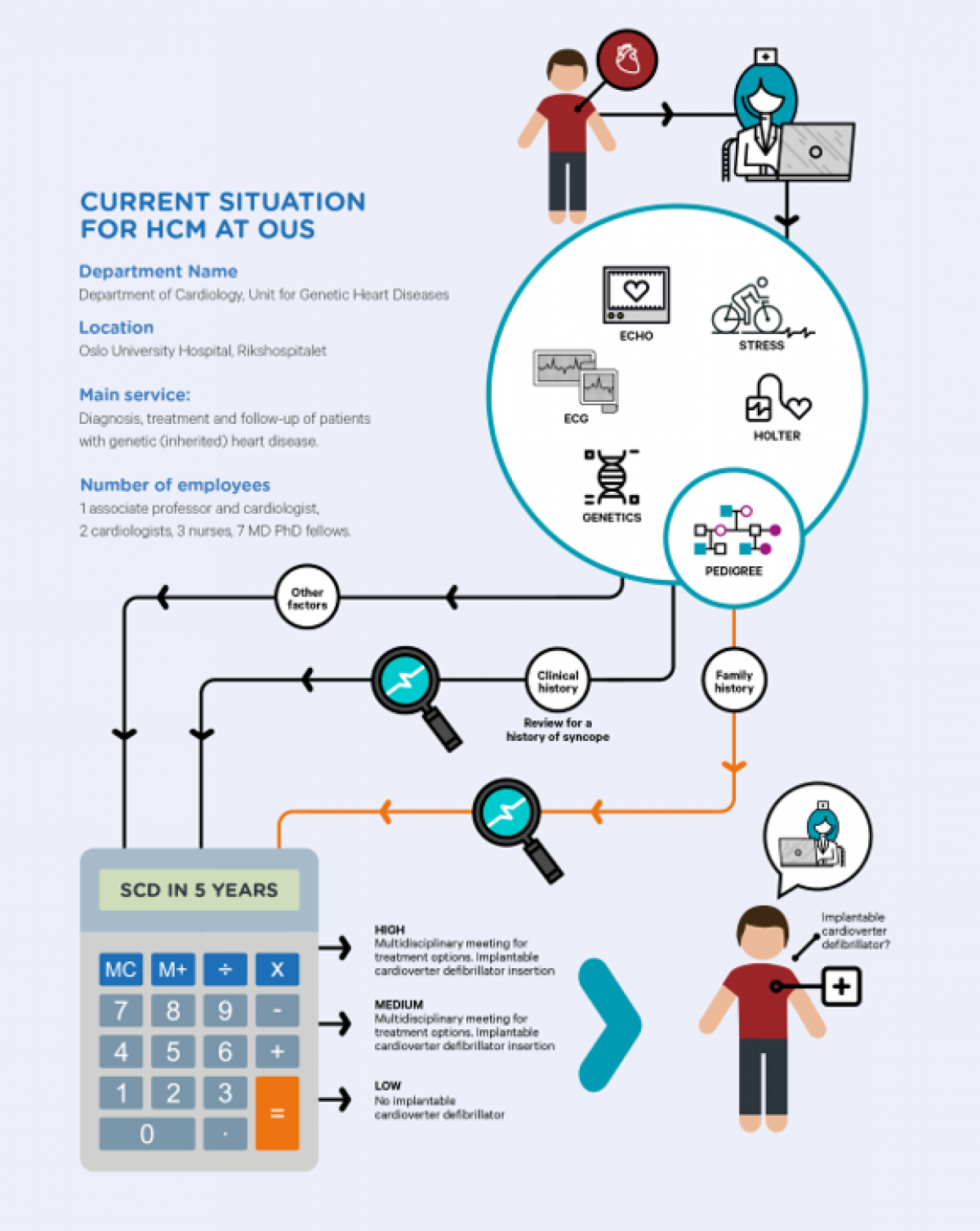
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the most common genetic heart disease, with disease-associated mutations found in 0.2-0.5% of European populations. HCM patients have an elevated risk of SCD, with several factors known to modulate individual risk.
Sudden Cardiac Death

Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) accounts for approximately 5,000 deaths yearly in Norway. High-risk individuals when identified can be offered life-saving therapy. Selection of patients for this therapy and prediction of SCD is one of the greatest challenges in current cardiology. Use of patient-specific genetic data combined with clinical data is instrumental in risk stratification for SCD.

Objective
The overall objective of the workpackage is to structure patients’ course through the chain of health care providers and support decision making for patients at risk of sudden cardiac death and of adverse outcome e.g. heart failure.
Activities
- NLP projects:
- Identification of patients at risk for SCD from electronic medical journal, identification of “syncope” to populate risk calculator.
- Interpretation of CT descriptions
- Pedigree tool: Extraction from free text - family relations relevant for medical condition
Deliverables:
- SCD Risk Calculator implemented in DIPS Arena
- Automatic echo measurements for input to calculator (machine learning)
- Pipeline for text extraction from electronic medical journal
Partners: OUS cardiology, Ahus, NTNU, UiO IFI Language Technology, Kunnskapsforlaget


Relevant Projects

Risk Calculator for SCD
A risk calculator which aids in patient risk estimation for Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) has been published by the European Association of Cardiology, and the BigMed cardiology work package has been tasked with automating and if possible

Functionality for clinical Natural Language Processing
Current state of the art solutions from the field of Language Technology employ machine learning algorithms and large volumes of data to solve tasks that enable understanding of textual data, such as the extraction of entities and

Big data management for the precise treatment of three patient groups

Regulation of CDS Software
The amount of health data used in patients’ diagnosis or treatment is growing beyond a manageable level for individual clinicians. Clinical decision support (CDS) software can help to access and analyse these data and thereby assist

